(On this day – May 21, 2021) President Rodrigo Duterte signed Republic Act No. 11550, a landmark legislation that divided the province of Maguindanao into two distinct provinces: Maguindanao del Norte and Maguindanao del Sur. This move was not just a redrawing of boundaries but a strategic effort to enhance governance and spur development in a region long plagued by political strife and economic challenges.
The Rationale Behind the Division
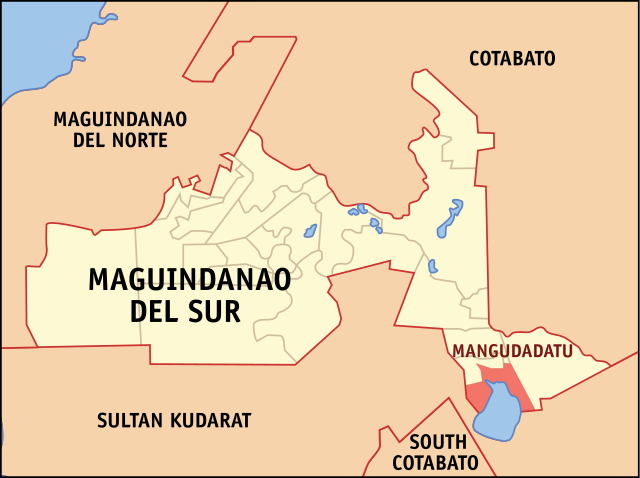
Maguindanao, located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM), has historically been one of the largest and most complex provinces in the Philippines. The province’s vast size and diverse population have often made it difficult to manage effectively.
By splitting Maguindanao into two smaller provinces, the government aimed to create more manageable administrative units that could better address the needs of their respective populations.

Governance and Political Dynamics
The division of Maguindanao was also seen as a way to address the entrenched political rivalries that have long characterized the region. The new provinces are now governed by two prominent political families: the Mangudadatus in Maguindanao del Sur and the Sinsuats in Maguindanao del Norte.
This division was expected to reduce conflicts by giving each family control over their respective territories, thus minimizing the chances of violent clashes.
Economic and Social Development
One of the primary goals of Republic Act No. 11550 was to accelerate economic and social development. Smaller administrative units are often more agile and can respond more quickly to local needs.
The division was expected to improve the delivery of basic services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. Local officials and political experts believed that two smaller provinces could pave the way for better access to resources and more focused development efforts.
The Transition Period
The transition to two separate provinces was not without its challenges. The plebiscite to ratify the division was held on September 17, 2022, and the proposal was overwhelmingly accepted by the electorate, with 99% voting in favor. However, the process of establishing the new provincial governments required careful planning and coordination.
Appointment of Officials
Initially, there was some confusion regarding the appointment of officials. The law stipulated that the incumbent governor of Maguindanao would become the governor of Maguindanao del Sur, while the vice governor would assume the role of governor in Maguindanao del Norte.
However, due to the timing of the plebiscite, which was held after the 2022 national and local elections, the Commission on Elections (COMELEC) had to issue a legal opinion. Eventually, the Department of the Interior and Local Government (DILG) appointed the first set of officials for the new provinces.
Establishing Governance Structures
The new provincial governments had to establish their corporate existence by appointing governors, vice governors, and provincial board members. This process included dividing assets, properties, and even debts between the two provinces. The transition period also involved setting up new administrative offices and ensuring that all provincial appointive positions were filled within 60 days.
The Impact on Local Communities
The division of Maguindanao has had a significant impact on local communities. For many residents, the split brought hope for a better future. They anticipated improved access to basic services and more effective governance. However, the transition also brought challenges, particularly in terms of political dynamics and resource allocation.
Political Landscape
The division solidified the political bases of the Mangudadatus and Sinsuats, allowing them to strengthen their influence in their respective provinces. While this move was seen as a way to reduce conflicts, it also raised concerns about the entrenchment of political dynasties.
Critics argued that the division could lead to increased bureaucratic exploitation and corruption, as well as intensified land-grabbing and militarization.
Economic Opportunities
On the economic front, the division was expected to create new opportunities for development. Local officials hoped that the smaller administrative units would attract more investments and spur economic growth.
The new provinces were seen as better positioned to manage their resources and address local needs more effectively. For instance, Maguindanao del Norte, with its rich fishing grounds and agricultural lands, was expected to leverage its natural resources for economic development.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the optimism surrounding the division, several challenges remain. The region continues to grapple with issues such as poverty, landlessness, and political violence. The success of the new provinces will largely depend on their ability to address these challenges and deliver on the promises of improved governance and development.
Addressing Poverty and Landlessness
Maguindanao is one of the poorest provinces in the Philippines, with a significant portion of its population living in poverty. The new provincial governments will need to implement effective poverty alleviation programs and address the issue of landlessness, which has been a major source of conflict in the region. Ensuring that farmers have secure land tenure and access to resources will be crucial for sustainable development.
Ensuring Peace and Stability
Peace and stability are prerequisites for economic development. The new provincial governments will need to work closely with the national government and local communities to maintain peace and order. This includes addressing the root causes of political violence and ensuring that all residents feel safe and secure.
The appointment of capable leaders and the establishment of effective governance structures will be key to achieving this goal.
Leveraging Natural Resources
Both Maguindanao del Norte and Maguindanao del Sur are rich in natural resources. The new provincial governments will need to develop sustainable strategies to leverage these resources for economic growth. This includes promoting responsible mining, agriculture, and fishing practices, as well as attracting investments in these sectors. By doing so, the provinces can create new job opportunities and improve the quality of life for their residents.
Conclusion
The division of Maguindanao into Maguindanao del Norte and Maguindanao del Sur marks a new chapter in the region’s history. While the transition has brought challenges, it also offers a unique opportunity for improved governance and development.
By addressing the root causes of poverty and conflict, and leveraging their natural resources, the new provinces can pave the way for a brighter future for their residents. The success of this endeavor will depend on the commitment and collaboration of all stakeholders, from local communities to national leaders.




Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks so much for the blog article.Really thank you! Really Cool.